Chapter 2: Remuneration components
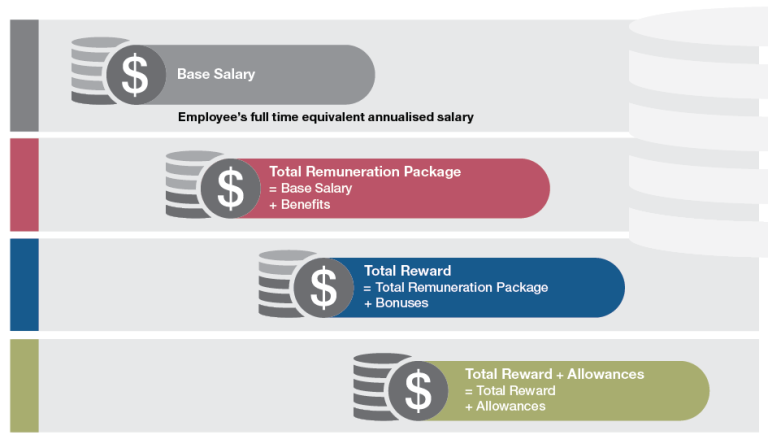
The key remuneration components covered by this report are Base Salary, Total Remuneration Package, Total Reward and allowances.
Base Salary
Base Salary is an employee’s full time equivalent annualised salary. It includes salary sacrifice amounts such as pre-tax employee superannuation contributions made via salary sacrifice arrangements.
Total Remuneration Package
Total Remuneration Package incorporates Base Salary plus benefits. Benefits include: employer superannuation contribution, motor vehicle cost, cash in lieu of a motor vehicle, motor vehicle parking, personal benefits and other supplementary payments.
Total Reward
Total Reward incorporates Total Remuneration Package (Base Salary plus benefits) plus bonuses. Bonuses include: performance, retention, productivity, sign-on, performance by the employee’s group or whole agency and fixed top-of-salary range payments.
Allowances
Allowances are payments that sit outside of Total Reward as Total Reward plus allowances. They cover payments for working conditions, qualifications and work-related expenses. The availability of, and eligibility for, allowances depends on specific conditions provided under an employee’s employment instrument and particular circumstances of positions.
Figure 2.1 Remuneration components
Movement in remuneration components
Remuneration movements are affected by a number of factors such as general wage increases, increment progression through salary scales, promotions, separations, engagements and transfers between agencies.
Increased numbers of engagements and promotions can affect median values as newly engaged and promoted employees tend to commence on salaries at or near the bottom of their salary scale.
Large agencies can have a substantial impact on remuneration movements. Services Australia, the Australian Taxation Office, the Department of Defence and the Department of Home Affairs make up 51% of employees covered in this report. Wage increases, differences in salary scales and changing recruitment patterns at these agencies can influence median percentage changes.
The population of each classification can also affect remuneration movements. A change in headcount can easily shift the median value in a salary range for classifications with a small population such as the APS 1, APS 2, Graduate and SES levels.
Figure 2.1 shows the annual proportional change in weighted median Base Salaries for non-SES and SES employees over the last five years. Some of the factors that influenced these changes are described in Chapter 3.
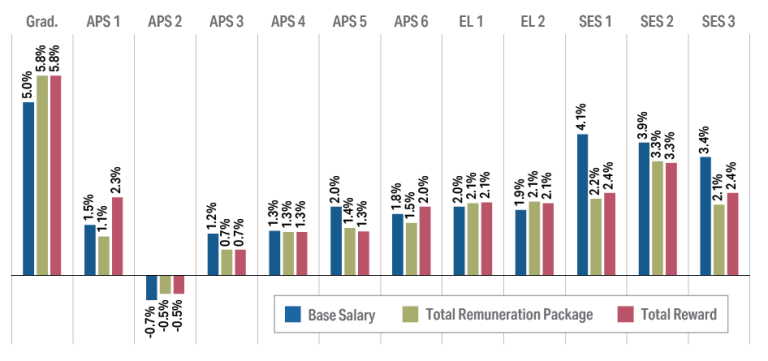
Figure 2.2 Percentage change in weighted median Base Salary by classification group 2018 to 2022
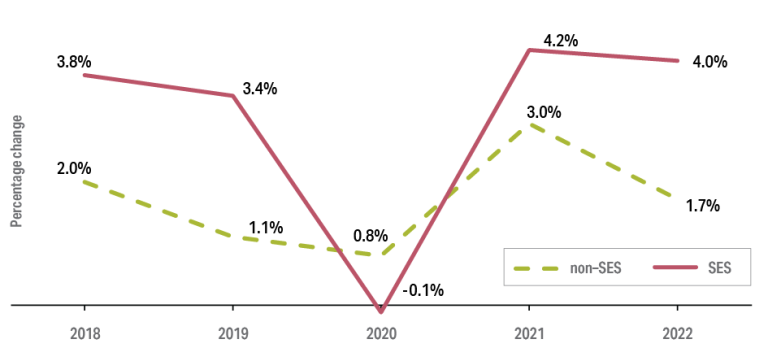
Figure 2.2 shows movement in median Base Salary, Total Remuneration Package and Total Reward from 2021 to 2022. There were increases across almost all remuneration components and classifications. APS 2 median movement was impacted by a large intake of new employees in one agency which lowered median remuneration for this classification.
Figure 2.3 Percentage change in median remuneration components, 2021 to 2022>